What Is Mastering in Music and Why It’s Important
What is mastering in music? Learn what audio mastering involves and why it’s essential to master your music.

What Is Mastering in Music and Why Is It Important?
Audio mastering is the final step in the music production process. It’s the post-production process of optimizing music and preparing it for music distribution.
The mastering stage involves signal processing with equalization, compression, saturation, stereo enhancement, limiting, audio restoration, and other final touches. Mastering engineers must also adhere to specific loudness standards when creating digital masters.
The purpose of mastering is to make your music sound balanced, cohesive, uniform, professional, and ready for commercial release. Mastering also ensures playback optimization across various speaker systems and media formats.
Stereo Mastering vs. Stem Mastering
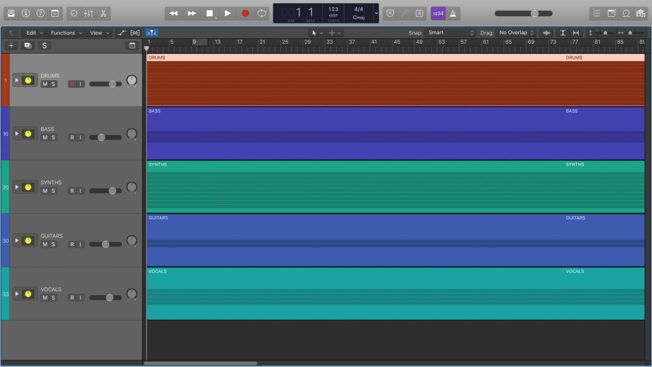
There are two methods of mastering: Stem mastering and stereo mastering .
What Is Stereo Mastering?
Stereo mastering uses a single stereo mix as its sound source. However, this method of mastering limits flexibility. For example, if you increase the vocal volume, you would likely also increase the volume of other elements. The same rule applies to EQ, dynamics, saturation, stereo imaging, and other processing.
However, the benefits of stereo mastering include cost and ease of delivering the entire project. Mastering a single audio file costs less than treating multiple files. Also, exporting, managing, and providing a single audio file is easier than dealing with numerous files.
What is Stem Mastering?
Stem mastering offers greater control over the shape and tonal balance of your music. This method uses multiple audio files called “stems” as a sound source. Stem files combine individual tracks into a single file. Typically, stems files include certain parts of the mix like drums, vocals, bass, synths, etc.
With stem mastering, you can process these separate tracks in isolation. This technique gives you more flexibility and convenience. For example, you can treat the vocal track without affecting the other elements in the mix.
After treating each stem, the mastering engineer will then apply finishing touches to the full mix. This approach often results in a more balanced, professional-sounding master.
Why Is Audio Mastering Important?
Mastering is a crucial step in the audio production process. For example:
Modern mastering ensures your music will sound the best it can across streaming platforms, media formats, devices, and speaker systems. Some formats include vinyl, CD, Tape, and digital audio files. While streaming services include Spotify, Apple Music, SoundCloud, and more.
Mastering also ensures the tracks on an album or EP have consistent volume levels. Matching levels for each track improves the listening experience. For example, you can listen to an entire album without adjusting the volume between songs.
Lastly, mastering prepares your music for distribution. This step includes sample rate conversion, bit depth reduction, sequencing tracks on an album or EP, adding required metadata, and more. The finished master file is then sent out for distribution and future replications.
How a mastering engineer treats a song depends on several factors. For example, their style, the audio format, music genre, loudness standards, intended distribution platform, and other reasons.
Artists and audio engineers master music to:
- Improve the sound quality of digital audio for an optimum playback experience.
- Emphasize or reduce certain frequencies to balance the frequency spectrum.
- Fix problematic audio frequencies, phase issues, and frequency response imbalances.
- Improve tonal balance by creating an even distribution of frequencies. A balanced frequency spectrum helps dynamic recordings translate on different playback systems.
- Manage dynamic range, control transient spikes, and increase loudness. Dynamic range compression also “glues” each element into a cohesive whole.
- Remove pops, clicks, and other unwanted noises from a sound source.
- Apply stereo enhancement to balance the stereo field and add dimension. Widening your mix will create a more focused low-end and help it sound bigger. It also improves the listening experience.
- Clean up the frequency range from low-end rumble and harsh high-frequencies.
- Increase the perceived loudness with limiting to reach commercial levels.
- Ensure the songs on an album or EP have consistent sound levels.
- Create fades or crossfades for smoother transitions between songs on an album or EP.
- Arrange songs into a final sequence for an album or EP.
- Add required metadata and ISRC codes into the digital file. They’re necessary for cataloging and tracking a song.
- Insert track markers for CD replication or any other digital medium.
- Apply proper bit depth reduction and sample rate conversion. Converting audio tracks is necessary for distribution and playback on digital mediums. The standard bit depth is 16-bit/44.1 kHz .
- Finally, having a mastered track is the standard requirement for record label releases.
[yuzo id=”13031″]
What Is the Difference Between Mixing and Mastering?

Mixing and mastering are separate stages in the creative process often conflated. These two stages can become blurred since today’s music producers wear different hats in the studio.
What Is Audio Mixing?
Mixing combines multiple layers of audio to make one final track. The mixdown process makes sure the individual elements in a song sound good together.
The audio mixing process involves:
- Balancing track levels
- Gain Staging
- Panning individual instruments
- Equalizing
- Compression
- Harmonics enhancing
- Correcting phase issues
- Improving clarity
- Fixing problems
- Adding audio effects
- Applying automation
- Editing sounds in creative ways
- Adjusting sound qualities
There’s a lot of technical understanding involved!
The goal is to treat the separate tracks of a song to create a cohesive mix that sounds amazing. The mixing engineer then exports the final mix as a stereo track file.
Typically, the mastering engineer will request an audio file with specific bit depth, sample rate, and headroom amount.
What Is Audio Mastering?
The mastering stage enhances the mixdown’s audio quality and prepares the entire track for distribution. This final step applies the same primary tools and techniques as mixing. For example, a mastering engineer will make slight adjustments to EQ, compression, saturation, stereo enhancement, and limiting.
However, the process involves making subtle changes across a signal chain on the master channel. A subtle change can make a huge difference in mastering. And if there are issues with the mix, it should go back to the mixing engineer.
The goal is to create a balanced frequency response, a controlled dynamic range, and a commercial loudness level. It’s also vital to establish consistent sound levels across each track. To help guide creative decisions, the engineer will use reference tracks.
These finishing touches create a high-fidelity stereo file ready for commercial release. Having a great sounding and balanced master is crucial!
Mastering Yourself vs. a Mastering Engineer

With advanced and affordable music technology, anyone can master music. And while there are mastering tutorials, nothing beats the expert ears of a professional mastering engineer.
Mastering is an art form that can take many years of practice to master (pun intended). Moreover, experienced mastering engineers have trained ears, musical intuition, expertise, pro audio equipment, treated rooms, and years of knowledge.
However, honing your mastering skills is encouraged. If you plan on mastering your music yourself, best first to strengthen your mixing skills. The mastering stage adds the final polish to a great sounding mix. You must prepare quality mixes first!
If you want a professional sound, go with a trained mastering engineer until you develop your mastering skills. Experienced ears and technical understanding will get your music to a level that competes with everything out there.
Plus, there are several affordable mastering studios and online mastering services like LANDR. Research your options.
Common Misconceptions About the Mastering Process
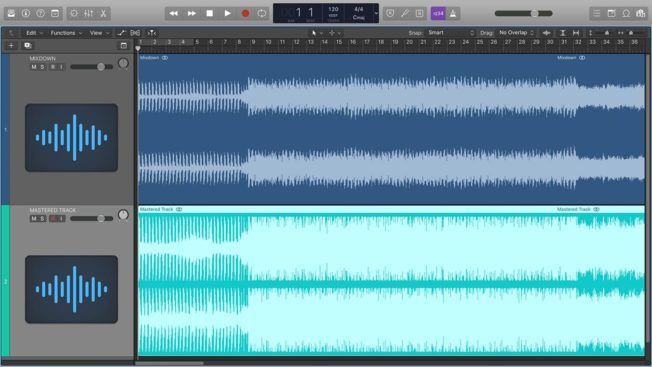
A common misconception is that a great master will make a bad mix sound good. Mastering will not fix a bad mix. Your mixdown must sound excellent before sending it out for mastering.
Also, mastering accentuates everything in your music. It makes the good parts sound great, and the bad parts sound terrible. Moreover, problems not fixed in the mixdown stage are hard to correct during the mastering process. So, don’t send your music out for mastering if you’re not satisfied with your mixdown. You may not like what your mastering engineer sends back. Also, don’t count on them to fix your mistakes!
Conclusion
Audio mastering will play a critical role in the success of your music. It’s a must if you want to stream music online, distribute CDs, or press a vinyl record. Think of this final stage as the bridge between your artistic vision and a world of listeners.
Also, mixing and mastering are both vital stages in the music creation process. It’s encouraged to learn the necessary knowledge, techniques, tools, and music industry standards.
How to learn mixing and mastering? Learn these critical skills through structured learning at ICON , online tutorials, and reading guides. Also, experiment with different mastering effects and signal chain configurations.
You can also connect with a mixing engineer or mastering engineer at a local recording studio. Sit in on a mastering session. Hands-on learning at a mastering studio with pro audio equipment will help hone your craft.