5 Exciting Careers in Music Business Worth Pursuing
Are you looking to pursue a career in the music industry? Check out these five essential careers in music business! They keep the music industry moving.

How to Get into the Music Industry?
The music industry has needs that go beyond the music itself. In today’s music job market, it takes business professionals to elevate music into a cultural phenomenon.
The music business is a vast, complex industry. It employs millions of people across different career paths. Everything from event production planning to music law.
However, it’s difficult to make a decent living in the music industry. Succeeding in music requires various disciplines, strategies, knowledge, and experience beyond creating or performing music. Versatility is key to a sustainable career in music!
Pursuing a career in music business opens doors to more opportunities. Plus, learning and practicing the business side of music is essential in this competitive industry.
Are you passionate about music and want to find a music related career path? Consider these five entry level music business careers:
5 Promising Careers in Music Business
This list of five career paths are perfect for those ready to pursue the hustles of music business.
1. Artist Manager
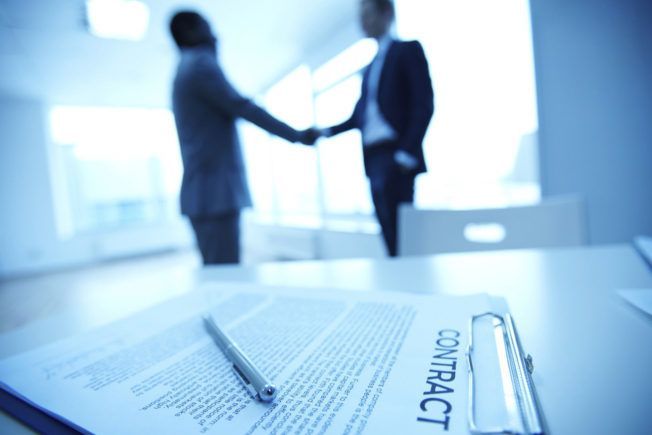

Behind each successful artist is a hard-working and talented manager. An artist manager plays a significant role in shaping an artist’s career.
An artist manager represents and serves as an advisor to their artists. They find opportunities, represent their interests, oversee day-to-day schedules, negotiate contracts, counsel them on career decisions, and more.
Artist managers are also the middleman between the artist and the music industry. They work on behalf of the artist, handling the business and professional development of their career. This allows the artist to maintain their mental health and focus on creating their art.
Depending on a manager’s style, they can also become a mentor to the artist. For example, teach them music business skills, music production techniques, mental health management, and more. This guidance will help the artist reach their full potential.
Professional Skills and Duties:
- Apply music business experience and strategies
- Help guide the artist development process
- Network with industry professionals and create a contact list
- Have excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Advise and guide career decisions
- Negotiate record label and licensing contracts
- Create marketing and merchandising strategies
- Manage day-to-day schedules and activities
- Oversee budgeting and money management
- Build relationships with record labels, music distributors, event promoters
- Handle music licensing, music publishing, and performing rights
- Plan and organize tours, events, and interviews
- Collect royalties, revenues, fees, and other payments
- Oversee the production and distribution process
- Help improve the mental and physical health of their artist
2. Tour Manager
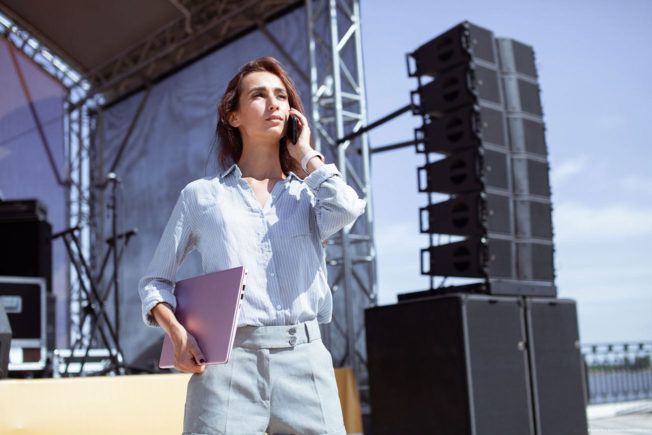

A tour manager (TM) travels with an artist and ensures the tour runs smoothly. They organize, plan, and manage various touring logistics.
The responsibilities of a tour manager change depending on the size of the tour. But certain aspects of being a TM remain consistent across any tour.
Professional Skills and Duties:
- Arrange travel plans
- Confirm reservations
- Manage tour finances
- Arrange transportation
- Make lodging arrangements
- Manage the tour schedule and set times
- Coordinate equipment needs, soundcheck, and set times
- Ensure everyone gets where they need to be on time
- Deal with promoters, venue managers, ticket agents, etc.
- Coordinate media and marketing coverage
- Network with industry professionals and create a contact list
- Demonstrate excellent leadership skills
- Work under pressure and meet demands
- Implement time management and organizational skills
- Demonstrate excellent communication and interpersonal skills
Another essential aspect of being a tour manager is keeping everyone happy and healthy. Touring is a demanding and stressful lifestyle. A good TM will make sure everyone is performing at their best.
Read how to survive the road as a touring artist. Find advice on how to plan your tour, take care of your health, and navigate the music industry.
3. Booking Agent (Talent Agent)
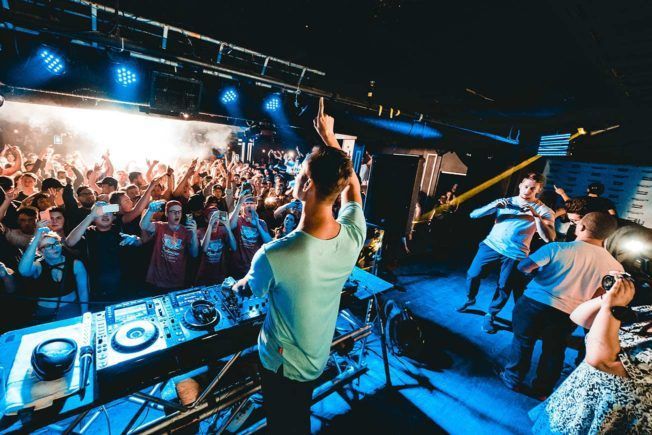

A booking agent’s primary responsibility is to book gigs for their clients. They’re the point of contact for talent buyers interested in booking an artist.
Booking agents also facilitate the logistics involved in securing live performances or appearances. This includes securing venues, negotiating details, arranging equipment needs, organizing hospitality, managing finances, and more.
Agents work closely with promoters, venues, festival organizers, record labels, and managers. They make sure the artist plays dates and venues that align with their capabilities, goals, and artistic profile.
Like a manager, a great booking agent will also build connections in the music industry. They can also work independently or for a booking agency that represents a roster of artists.
Moreover, having industry connections allow booking agents to advance their clients’ music careers. These advantages are also a big reason artists sign with a particular agent or agency.
Professional Skills and Duties:
- Search for new talent to represent
- Find and secure live performances or appearances for artists
- Locate and secure appropriate venues for artists
- Negotiate artist fees, contract terms, set times, and guest lists
- Develop connections with talent buyers, venues, and promoters
- Arrange hospitality, transportation, and hotels
- Arrange equipment needs, soundcheck, and other technical requirements
- Liaise with the artists’ management team to agree on logistics and goals
- Network with industry professionals and create a contact list
- Manage ticket sales and related finances
- Manage marketing and promotional strategies
- Coordinate media coverage, appearances, and interviews
- Demonstrate excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Implement time management and organizational skills
- Help increase the artists’ exposure within the music industry
4. Record Label Manager

A record label manager coordinates and oversees operations at a record label. They implement a release schedule, manage contracts, coordinate marketing strategies, manage royalties, and more.
A label manager also guides the entire musical project from early planning to the release. They work with the A&R department, the label’s artist roster, management teams, and digital music distribution services.
However, the manager’s role varies depending on the size and budget of the record label.
For example, at a smaller, independent label, the manager can serve as A&R and various other roles. With a major label, the manager focuses on more big-picture planning.
A major label will have separate departments for A&R, marketing, design, distribution, and more. This structure allows the manager to delegate smaller tasks to individual departments.
Professional Skills and Duties:
- Develop and maintain relationships with the label’s artist roster
- Manage the entire music project from planning to release
- Maintain and update a release schedule
- Distribute and manage artist contracts
- Manage the label’s budget, artist royalties, and various fees
- Oversee the different departments depending on the size of the label
- Delegate tasks to the departments and ensure timely delivery of release assets
- Network with industry professionals and create a contact list
- Manage the digital music distribution account
- Plan the release strategy and monitor analytics
- Manage marketing and promotional strategies
- Coordinate media coverage, appearances, and interviews
- Demonstrate excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Implement time management and organizational skills
- Oversee non-music relate aspects of running a business
5. A&R Representative
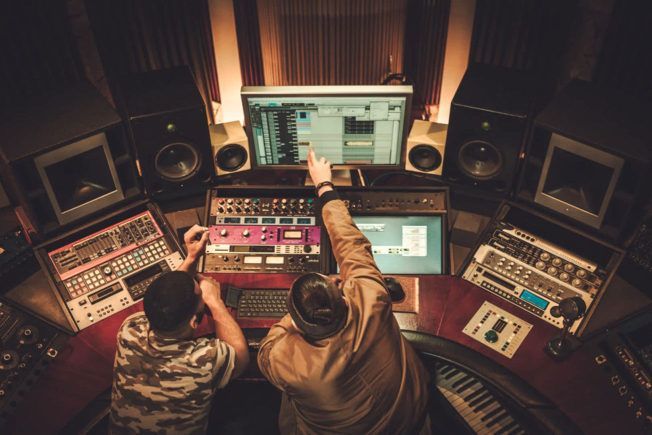

A&R stands for “ Artists & Repertoire.” It’s the A&R’s job to find and curate new talent for record labels.
A&R’s continually search the internet for up and coming artists. They also talent scout at various shows and festivals. That’s how they stay up-to-date with what sounds and styles resonate with the music community.
The first part of the A&R rep’s job is finding artists they want on their roster. Then they approach them with a record contract offer and convince them to sign.
The A&R will also help facilitate the recording and production process. It’s their job to give them the platform that best fits the particular artist’s needs.
Also, an A&R is most valuable to a label when they identify artists ready for success. The next big thing!
Up and coming artists are much more open to contracts. Plus, it’s a massive boost for business if the label finds a huge star early in their career.
Whereas artists who established huge success have more leverage. This makes it more challenging to secure a record contract.
Professional Skills and Duties:
- In-depth knowledge of musical trends, movements, and styles
- Have an exceptional ear for music
- Talent scout and oversee the artistic development of artists
- Network with industry professionals and create a contact list
- Maintain an artist roster and a release schedule
- Understand and manage artist contracts
- Manage and oversee budgets of new music projects
- Demonstrate excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Liaison between the artist and the record label or publishing company
- Spend time listening to music, scouring clubs, watching social media, reading music blogs
- Represent an artist’s interests within the record label
- Help guide the artists’ subsequent career
- Find music collaboration opportunities
- Organize promotional and marketing efforts
- Supervise the entire recording process
How to Get into Music Business?
ICON’s Music Business Program prepares students for various jobs in the music industry.
A vital aspect of the program focuses on developing fundamental music business skills and strategies. Students then apply what they learned in real-life music business situations.
Music Business students also work alongside students from the Music Production Programs and Vocal Artist Program. They apply the knowledge taught in the classroom to help vocalists and producers develop their careers.
Learn everything you need to know about the music business. This extensive program teaches you how to:
- Establish core fundamentals of the music business
- Navigate and succeed in the ever-evolving music industry
- Protect intellectual property and understand copyrights
- Understand music law and complex contracts
- Develop an artist’s brand and create revenue streams
- Establish an understanding of publishing, licensing,
Performing Rights Organizations, touring, and branding - Manage and implement music media, social media, merchandising, promotion, and marketing strategies
Students will also partake in professional, hands-on music business internships. Internships benefit those seeking entry level music industry jobs.
ICON will also connect students with notable entities in the music industry. This gives them a chance to apply their knowledge in real-time. ICON has relationships with management companies, record labels, PR firms, and more.
Graduates of the Music Business Program will leave with prospective clients and industry contacts to kick-start their careers.
Jumpstart your music career today! Check out ICON’s Music Business Program. You will get a comprehensive music industry education, unlike any other music business college.
Conclusion
The music business requires more than musicians to advance. While the musicians get most of the attention, there are roles in the music industry equally vital.
Someone on the business side of things could have a significant effect on the future of music. As long as they have an unwavering work ethic and the right skills.
That effect can take various forms. For example, a great manager could develop the next Led Zeppelin. A talented agent could secure an all-star lineup for the next Woodstock. While the next wave of A&R reps will find the new generation of hitmakers.